Info-Cafe
Results for : All categories
Results for : All categories
Non Banking Financial Company – What it is and How to Apply for it?

A non banking financial company (NBFC) can be defined as a financial institution that is known to provide some financial services that are provided by the banks as well, the major difference being that they do not have a banking license as such. Normally, these institutions do not have the right to take deposits from common people.
This means that they are not under the purview of the oversight and regulation that you need traditionally for banks. NBFCs are allowed to offer banking services such as credit facilities and loans as well as retirement planning products. It can operate in money markets and can underwrite. It is allowed to perform merger activities too.
A little more information on NBFCs
In the United States of America (USA); it was under the Dodd-Frank Act that the NBFCs were formally classified as companies. They are basically supposed to take part in financial activities but for this to happen at least 85 per cent of their consolidated assets or yearly gross revenues have to be financial in nature. In fact, a lot of companies can be classified as NBFCs. This includes the following:
- Credit Unions
- Private Equity Firms
- Insurance Companies
- Mobile Payment Firms
- Money Market Funds
- Microlenders
- Asset Managers
- Peer to Peer Lenders
- Hedge Funds
How to start such an organization in India?
In India, the workings of an NBFC are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI); which also happens to be the apex financial institution of the country. Their main business is lending and acquiring shares, bonds, and stocks. They also do work such as hire purchase and financial leasing.
Normally as per the laws, in India an organization is thought to be a financial service provider when the financial assets of a company are more than 50 per cent of the aggregate asset base – similarly when earnings from financial assets make up more than 50 per cent of a company’s gross income.
If a company fulfills both these requirements it would need to have an NBFC license. In fact, the test needed to get such a license is known popularly as the 50-50 test. In India, these companies are not supposed to need an NBFC license:
- Agricultural Operations
- Providing Purchases and Services
- Industrial Activities
- Building and Selling Immovable Property – this could be the main business as well
- Selling and Buying Goods
- Any Small Financial Activity
Registration process is being simplified for new NBFC in India
Nowadays RBI made easy to register a new NBFC (Non Banking Financial Company) in India by minimizing the application form and checklist of documents. Earlier it was taking 45 numbers of documents to be submitted for registering a Non-Banking Financial Company but, now the applicant can submit approximately seven to eight documents during the revised application process.
Now the registration process of Non Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) is just become easy and smoother, as said by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
As said by the RBI, there are two distinct types of requisition context for non-deposit taking organization/NBFCs (NBFC-ND) based on the source of funds and customer interact (interaction between the customer and organization).
Types of NBFC companies
Here you can find the two different types of NBFCs functions are categorized into First Type and Second Type. The first type is referred to Type-I (not accepting deposits) and second type as Type-II (accepting deposits).
In Type-I, the NBFC-ND will not accept the funds from public and also have not to make customer interface for their future intention.
If the Type-I companies wants to avail funds from public or intend to make interaction to their customer for future purpose, they must have to take acceptance from the Department of Non-Banking Regulation under Reserve Bank of India.
In Type-II, the NBFC-D (the Non Banking Financial Company with deposits) will accept the public funds and also can make interaction with the customer for their future scope intention.
How to apply for an NBFC license?
If you want to get NBFC license, you would have to submit your application both offline and online at the regional office of the RBI. You would need to provide the latest information about the management of the company. You would have to provide certified copies of the Certificate of Incorporation.
In case, you are already a public limited company or wish to operate as one you would have to provide a certificate of commencement of business. You would also have to provide certified copies of the latest articles and memorandum of association of your company.
You would also need to provide the latest details of various clauses in said memorandum that may be related to your financial business. You would also need to provide a copy of your PAN (permanent account number) or CIN (corporate identity number) that has been allocated for your company.
You would also need to provide information regarding the director’s profile, which has to be filled up and signed separately by each and everyone on the board of directors of your company. If the directors already have experience of working in NBFCs they would need to provide certificates from those.
Essential documents required for getting NBFC license
These are the main documents required for NBFC registration in India:
- Certified copy of company incorporation certificate
- Certified copy of company MOA and AOA
- Detail information of all directors and shareholders of the company
- Board resolution in favour of NBFC registration
- Bank Account with minimum paid-up capital INR 2 Crores of the company
- A comprehensive action plan and activities about the company and proposed NBFC
- Financial statements of the company
- Director’s report and Auditor’s report
- PAN of the company
- Highest qualification of all the directors of the company
- We may request you, if any relevant document is required
Procedure to Apply for Getting NBFC License
To get your NBFC Company registration certificate form RBI, you need to apply the proposed company for NBFC license online and after the application process is completed, you have to submit the physical copy of application to the Regional Office of the Reserve Bank of India along with the essential documents.
A brief note on application process:
- First setup a Private or Public Limited Company
- Prepare a business plan with clear documentation
- Submit application online through COSMOS official portal
- Submit applied physical copy of application to RBI
- Track the status of application
So, here you can follow the steps of application process as explained below:
- First log on to the RBI secure site https://cosmos.rbi.org.in for NBFC application
- Click the “Click here” link for NBFC company registration which is just below the Username and Password. Don’t get confused by seeing the Username and Password section, that doesn’t required for NBFC, it is for other purposes. After clicking the Click Here link, a new window will open, bearing with the Excel Application Form for NBFC and SCRC.
- Now you can download the suitable Application Form (NBFC or SCRC) according to your need and filled it properly. Remember, during the filling of Excel Form; indicate the correct name of the RBI Regional Office in the field “C-8” of the “Annex-I Identification Particulars”.
- Upload the filled form by selecting the correct Type of Company in the same window upload section. After uploading the file, then you would get a Company Application Reference Number for the application of Certificate of Registration (CoR) for your company to be filed online. After this, you will have to submit your hard copy of application form of the company along with the necessary documents, mentioning that this is our company online application reference number at the concerned RBI Regional Office.
- You can check your status of the application on the same site address by inputting your acknowledgement number. Usually, the timelines for NBFC registration takes 45 days to get approval from the regulatory authority.
Timeline and expert help on NBFC
As you know, obtaining NBFC registration in India is completely depends on the RBI permission. And you can acquire your NBFC registration certificate from RBI in 90-120 days (3-4 months). And we will help you in this regard. As we are specialized in legal and financial advisory services in Bangalore and offer dedicated legal, incorporation, taxation and compliance services to startups, small and medium sized businesses in all over India. Our goal is to provide class-one solutions to all in one-stop shop.
If you want to know any more about on NBFC, then do touch with our experts, they can assist you at any moment during the office working time.
-------------------------------------
Related Articles:
How to Start a Startup in Bangalore?
How to Open a SEBI Registered Portfolio Management Company

A certain procedure needs to be followed in order to start a portfolio management company in India. First of all, you need to register it with SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India). The applicant needs to pay an application fee that amounts to INR 1 lakh and happens to be non refundable as well.
The money has to be paid through a demand draft in favor of SEBI and the amount needs to be paid in Mumbai. The application contains a form – Form A – and the applicants need to provide some extra information with it as well.
This extra information can be found at the official website of SEBI – www.sebi.gov.in. The applicants need to send the application at the address given below:
Head Office (HO) Address of SEBI at Mumbai, Maharashtra
Investment Management Department - Division of Funds- 1
Securities and Exchange Board of India
SEBI Bhavan, 3rd Floor A Wing,
Plot No. C4-A, ‘G’ Block,
Bandra-Kurla Complex,
Bandra (E), Mumbai - 400 051
Tel: +91-22-26449000 / 40459000
Fax: +91-22-26449019-22 / 40459019-22
E-mail: sebi@sebi.gov.in
Toll Free Investor Helpline: 1800 22 7575
This consumer helpline number is working through the Interactive Voice Response System (IVRS) technology as communication takes place through computerized voice of interaction.
If you are looking for any information relating to SEBI in your local regional office in Bangalore, then you can contact us or visit this address below:
SEBI Bengaluru Local Office, Karnataka
Securities and Exchange Board of India
2nd Floor, Jeevan Mangal Building,
No. 4, Residency Road, Bengaluru – 560025,
Karnataka, India
Tel: +91-080-22222262/ +91-080-22222264/ +91-080-22222283
E-mail: bangalore-lo@sebi.gov.in
Capital adequacy requirements and some other things to be kept in mind
In order to become a portfolio manager in Bangalore India, the base net-worth of an applicant/ portfolio professional manager has to be INR 5 crore (previously it was Rs 2 crore, now increased to Rs 5 crore) and it is going to implement from January 2o2o. It also needs to pay a registration fee of INR 10 lakh. This needs to be paid when SEBI grants it the certificate of registration.
Validity & renewal of certificate
The certificate is supposed to remain valid for a period of 3 years. The applicant would have to apply for renewal at around 3 months before of its expiry date, if he/she wishes to continue as a registered portfolio manager.
For renew of its registration, the applicant has to pay Rs. 5 lakhs to SEBI as renewal fee.
Laws regarding contracts between portfolio managers and clients
SEBI specifies that before a portfolio manager takes up any assignment to manage funds or a portfolio of securities as a representative of its client they both must enter a contract. This agreement has to be reached in writing. This agreement would define clearly the relationship that both of them would share.
It would also mention clearly their mutual rights, obligations, and liabilities that are connected to managing the portfolio of securities and funds. The Schedule IV of SEBI (Portfolio Managers) Regulations, 1993 mentions some details regarding such agreements and they have to be there in said agreement.
What fees can be charged by a portfolio manager?
SEBI has not fixed any upper limit – or even any scale for that matter – as far as the fees to be charged by portfolio managers in India is concerned. However, the regulations also mention that the portfolio manager should charge the fee that has been specified in the contract between it and its client.
The fee could be anything – it could be a certain fee or a fee that is based on returns. Even a combination of both is allowed as well. The portfolio manager however needs to seek permission from the client before charging the fee. The portfolio manager may provide its service directly or indirectly. The term indirectly implies that it is outsourced to another similar entity. Even then, it can charge a fee for its work.
Value of funds and securities
As per the rules and regulations of SEBI, a portfolio management services in India would not be allowed to work with funds lesser than INR 5 lakh or securities whose value is lower than that particular figure. Also, a portfolio manager is not allowed to borrow money on behalf of its clients. It can only invest their money.
It also needs to be kept in mind that if an investor wants to put its money on listed securities under a recognized stock exchange then he/she would have to open one demat (dematerialization) account for PMS services.
The account also needs to be opened in its own name and give power of attorny to portfolio money manager in favor PMS to manage the funds. A portfolio manager is also supposed to provide regular reports as agreed to in the contract reached with the client.
Client expects reports from portfolio manager
As per the agreement in the contract, the portfolio manager shall provide the report to the client at a regular occuring interval and it should not be exceeding more than six months.
Can investors allowed to withdraw their premature funds/securities?
Yes, the funds or securities can be withdrawn by the investors before the maturity of contract. But, it depends upon both the investor and portfolio manager’s agreement regarding premature withdrawal.
Can a portfolio manager offers guaranteed returns?
No, a portfolio manager can’t promise to offer a guaranteed return on client’s investment.
Minimum investment amount required for investor in PMS
Recently, SEBI has increased the minimum investment limit for investor in a portfolio management service (PMS) to Rs 50 lakh from Rs 25 lakh earlier and it would be applicable from January 1, 2020 onwards. So the investors need to bring Rs 50 lakh to invest in a PMS.
------------------------------------------------
How to Register/Incorporate Company in Bangalore India?
How can Foreign Investors Invest in Indian Company

You might be a non resident Indian (NRI) or a foreigner who is looking to make a play for the market in India for some reason or the other. Quite often, as a foreign investor you may also be eager to know about the various ways in which you are able to use the money that you have in India and just grow it. You would be happy to know that there are several ways in which you would be able to invest in India even if you are not an Indian national.
Here you can follow some investment plans that are providing services to non-resident Indian (NRI) for investing in Indian company and abroad.
Foreign direct investment
Foreign direct investment (FDI) is the easiest way for one to invest in India in case that entity is not Indian. There are however certain activities and sectors where you will not be allowed to do this as such. Investments such as these are normally done under the aegis of the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA). India has an FDI policy as well, which places caps on certain sectors. There are two major ways through which this can happen – the automatic route and the government route. There are certain sectors and activities that are covered specifically by the two routes. Ones that cannot be done through the automatic route can be done via the government route.
The investment options open to you through the automatic route are normally strategic investments that have to be done over the longer term. In case of the government route the main authorities are the Foreign Investment Promotion Board (FPIB).
Foreign portfolio investment
You can invest in India as a foreigner through the various portfolio investment schemes (PIS). However, for that you need to be eligible – the only kinds of entities that are allowed to perform investments such as these are foreign institutional investors (FIIs), persons of Indian origin (PIO), NRIs, and qualified foreign investors (QFIs). They can invest in the convertible debentures and shares of Indian companies, the stock exchanges of India, and units of various mutual funds operating within India. An FII is basically an institution that has been incorporated outside India.
Foreign venture capital investors
A foreign venture capital investor (FVCI) is an entity who is established or has been incorporated outside the country. They are allowed to invest in domestic venture capital (VC) funds as well as VC undertakings. The latter are basically unlisted companies operating within India. In case you want to work as an FVCI in India you would have to procure separate registration from SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India). You would also need to invest at the very least 66.67 per cent of your investible funds in equity linked instruments and unlisted equity shares.
Other kinds of investments
NRIs can invest in various government securities in India – the same facility is afforded to the FIIs as well. Apart from this they can invest in any or all of the following options by companies in India:
- Treasury bills
- Commercial papers that have been issued by companies based in India
- Listed non convertible debentures
- Units of mutual funds based in India
- Bonds
There are however a few restrictions that are applied in these cases by the RBI.
Non repatriable investments
These options are meant only for PIOs and NRIs. In this case they can buy shares in Indian rupees – the investment can be done through an NRO (nonresident ordinary). In case you invest in these non repatriable investment options your earnings would be sent to the NRO account that you have opened for this purpose. By definition, the amount that you have invested in this scheme and the capital profits that you have made from the same cannot be sent outside India.
Digital Signature Certificate – What it is and How to get it?

The term digital signature certificate (DSC) can be defined as the electronic version of a paper certificate or a physical one such as a driving license or passport. They normally serve as proofs of identity of a person and are used in certain cases only. It is just like a passport that demarcates the country whose citizen you are. Thanks to your passport you can legally travel to a country.
In much the same way you can use a DSC in order to prove your identity as such in an electronic context. With the help of your DSC you would also be able to get access to technology as well as various other services on the internet. You can also sign various documents digitally as well.
Types of Digital Signature Certificate (DSC)
The different types of digital signature certificates are classified as 3 classes such as –
- Class 1 DSC: This signature certificate is issued and used for private/ individual’s purpose to identify and confirm the person’s name, contact details information subjected to verified against in database of certifying authority.
- Class 2 DSC: This signature certificate is issued and used for both business and individual personnel like director/partner/signatory authorities of the companies to represent and sign on various electronic documents.
- Class 3 DSC: This is the highest level authenticity DSC issued for organization/ individual’s to participate in e-commerce auction or online tender signing.
Where these DSCs are being used?
The organizations or companies or individuals are required DSC for the purpose of –
- Filing ROC in MCA portal
- GST filing
- Income tax filing
- Trademark & Patent
Why are DSCs important?
With the help of a DSC you would be able to authenticate your signature electronically. You also get a high amount of security by using this in the context of your online transactions. This digital signature makes sure that the information, which you exchanged during a particular transaction, remains absolutely private. The certificate can also be used to encrypt information in such a way that only the intended recipient is able to read it.
When you sign in any documents digitally or electronically, you're basically assuring the addressee that no information has been misrepresented in as an interim measure. The DSC also helps you verify your identity as far as being the sender of said message is concerned.
How to obtain DSCs in India?
As far as India is concerned, the legally valid DSCs are issued by certain entities. The highest among them is the Controller of Certifying Authorities (CCA). Next in line are the certifying authorities (CAs) who have been licensed by the Indian government. A prominent name among them is eMudhra. You can get secure digital signatures from them.
There are different options over here that are supposed to suit the requirements of different kinds of individuals as well as organizations. As far as the application process is concerned, you can easily visit the official website of eMudhra and find out as to how you need to apply for the DSCs, it is nicely said by ClearTax.
There are number of vendors who have Certifying Authority like Emudhra, Ncode Solution, Sify, etc
If you're looking for any kind of DSC for your personal or business use, we will help you to obtain your DSC in Bengaluru, Karnataka or anywhere in India. Because you know that most of the works are done online in these days.
Procedure for Obtaining Digital Signature
- Print Application Form as per your requirement
- Complete the documents as per listed below with self attested copies
- Send all the scan required documents
- After confirmation, please make payment the necessary fees
- Confirmation of SMS or Video
- Send document by courier or ask for pick up
- Download your Digital Signature Certificate through online using code
Documents Required for Obtaining Class 2 Individual
- ID Proof of Applicant (as Aadhaar/ Voter ID/ PAN Card/ Passport, Driving License)
- Address Proof of Applicant (Bank Account Statement, Utility Bill, Passport, etc.)
Documents Required for Obtaining Class 3 Digital Signature for Organization
For Limited/Private Limited/OPC/LLP/Partnership/proprietorship with seal and sign
- PAN Card of Applicant
- PAN Card of Organization
- Certificate of Incorporation
- Authorization Letter
- Application Form
- Current Account Bank statement
- MOA and AOA or LLP Agreement or Partnership deed or Proprietorship certificate
How are DSCs used?
The DSCs are used in a wide array of areas. You can use them in order to send and receive mails that have been signed digitally and are encrypted. They can be used in order to execute safe and sound transactions on the internet.
In fact, DSCs are also used in order to identify the other entities that may be taking part in a web-based transaction. You can use it for purposes such as eTendering and eProcurement. The DSCs are also used in order to file compliance with the Registrar of Companies in Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
If you wish to file your income tax returns on the internet then too you can use the DSCs. People also use DSCs in order to sign documents such as MS Word, PDFs, and MS Excel. If you wish to create a paperless office then this is easily the best bet that you got.
Are DSCs legal?
Ever since the Information Technology Act 2000 was enacted the DSCs have become legal in India. In fact, the CAs that issue these certificates work under the aegis of the Ministry of Information Technology of the government of India and it is the Information Technology Act that governs the entire procedure.
You should not though confuse a digital signature with a DSC. A digital signature is basically an electronic way of signing an electronic document. On the other hand, a DSC is basically a computer based record.
----------------------------------------------------------
Related Articles:
Know More About Director Identification Number (DIN) & How to Get It?
What is Director Identification Number & How to Get DIN

DIN (Director Identification Number) can be described as a unique identification number (UID) much like the Aadhaar number. This one too is issued by the central government and is allotted to individuals who are looking to become a director of a company or is already an existing director of a company. This unique identification number will remain valid for a lifetime. All the information pertaining to the directors are updated in a central database and maintained over there and this is done through the DIN.
The specialty of DIN is that it would belong to one person even if she or he were a director at more than one company. Even in case if she or he left a company and joined another one this number would stay with her or him.
Why is DIN necessary?
The DIN is needed in order for a director to sign on returns, applications, and information that may be related to a company and is supposed to be submitted by the company as per some law. The DIN is normally mentioned below the signature of the director in such cases.
How to get DIN in India?
An important part of the process of getting DIN in India is to apply for the same. If any directors of the company intend to obtain Director Identification Number (DIN) in India, he shall have to make application in eForm DIR-3 through online on MCA portal.
For this, you would need to fill out a form electronically. Then you need to sign it electronically and upload it on the official portal of MCA21 (Ministry of Corporate Affairs). Here is the link of MCA Services Login Portal. There are certain documents that need to be attached to the DIR 3 form such as your photograph, your identity proof, your residence proof, and verification. Now, under verification you would need to provide the following information:
- Name
- Father’s name
- Present address and permanent address
- Date of birth
- Place of birth
- Education qualification
- Mobile number and mail id
- Occupation
- Physical signature of applicant in all the attachments
In case you are not an Indian citizen you would have to submit your passport as the identity proof.
Your photograph, proof of residence, and proof of identity need to be attested by a chartered accountant, a cost accountant, or a company secretary. It is also essential that the professional doing the honours is a full-time professional.
As far as foreign nationals are concerned the attestation can be done by a foreign public notary or the Consulate of the Indian Embassy.
Once you have uploaded DIR 3 you would need to pay the fee at the next window screen. It needs to be paid via net banking, NEFT (National Electronic Funds Transfer), and credit card. You will not be allowed to make the payment manually.
After you have paid the application fee and submitted the application, an application number would be generated by the system. And DIN Allotment Letter will send to the respective person. The application will be processed by the national government and a decision will be taken on approving or rejecting it.
In case your application has been approved, you will receive communication from the central government having made the application.
In case the application has been rejected, you shall also come to know of the reason of rejection through an email. The reason behind your rejection would also be put up on the website. You will be given 15 days in order to correct the reason. In case you are able to accomplish that particular goal you will be allotted your DIN else your application would be declared invalid by the central government.
You also need to inform all the companies where you are working as a director your DIN within a month of getting it. You would also need to inform the ROC (Registrar of Companies) within 15 days of having intimated your company/ies.
--------------------------------------------------------------
Also Read:
Procedure Taken to Incorporate a Company in India
Company Formation/Registration/Incorporation in India
Incorporation of Company in India – Procedure and Steps Involved

As far as India is concerned companies are formed as per Companies Act, 2013. It has been said in the section 2 (20) of this Act that only those organizations that are formed as per said Act. It has given a definition of companies saying that company is an incorporated association that is in essence an artificial individual, possesses a separate legal entity, has eternal succession, a common seal, and a common capital that has been made up of limited liability and shares that can be transferred.
Following are the various kinds of companies that can be formed as per Companies Act, 2013.
Public Limited Company
Section 2 (71) of the Companies Act defines a public limited company. It says that a public limited company is one that has a paid up capital of at least INR (Indian National Rupees) 5 lakh and is not a private company. A company such as this does not limit the transferability of shares. As per rules you need at least 7 members in order to form such a company. However, there is no upper limit as such regarding the number of members that such a company could have.
Such a company is also required to have a minimum of three directors. Its name also needs to end with the word limited. It has the right to accept public deposits and can also invite the public to subscribe to its debentures and shares. Even in case this public company opens a private company as its subsidiary the Act will regard it as a public company.
Private Limited Company
Section 2 (68) of the Companies Act defines a private limited company. In order for a company to be recognized as a private limited company it needs to have a minimum paid up capital of INR 1 lakh.
The company operates under a number of restrictions that have been mentioned in the Articles of Association and Memorandum. There are limits on the number of shares that can be transferred between members. There cannot be more than 50 members. It cannot invite or accept public deposits, and cannot also invite the public to buy its debentures.
However, it does enjoy some privileges as well. It can be started with as little as 2 members. There is no need for it to create a prospectus and it can get started right away after it receives the certificate of incorporation.
One Person Company
A one person company is one that has only one main owner. This owner possesses the entire amount of the company’s share capital. Normally, in these cases a few dummy members are selected just in order to meet the statutory requirements in India pertaining to the minimum numbers of people that should be there in a company. It needs to be incorporated as per Section 2 (62) of the Companies Act. In these cases, the owner enjoys limited liability – the other dummy members are given a share each.
Limited Liability Partnership
In India, limited liability partnerships (LLPs) are registered as Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008. You need at least two partners in LLPs but there is no upper limit as far as owners are concerned. Here the share can be transferred but the transferee is not allowed to automatically become a partner as such.
How to incorporate companies in India?
Following are certain steps that you need to follow in order to incorporate companies in India:
- Get DIN (Director Identification Number) for the proposed directors for your new company
- Get DSC (Digital Signature Certificate) for the proposed directors of your company
- File the proposed name of your company with the Registrar of Companies (ROC) for its approval.
- Upload the spice form 32, form 33 – MOA, form 34 – AOA electronically
- Get the certificate of incorporation with PAN and TAN
- Ask for the Certificate to Commence Operation in cases where applicable
Here you can look over the process of company registration in India. To get a brief knowledge of everything on company formation here we explained shortly to register a company with the 7 steps. The following below steps are must needed to incorporate a company in Bangalore Karnataka and all over in India.
Let’s starts the company registration procedure using these 7 steps:
Step-1: Select the Type of Company – Choosing the right business structure is an important decision for you which will help your enterprise drive efficiently and meet your business goals and visions that you want.
Step-2: Apply for Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) – It is an electronic certificate refers to the identity of a person as like as passport or driving license. DSC is used in certain cases for signing the various documents in digital medium.
Step-3: Apply for DIN (Director Identification Number) – It is a unique identification number which is allotted to director of the company according to Section 152, 153, 154 of Company Act, 2013. DIN is mandatory for all directors.
Step-4: Apply for Name Approval – Company shall give proposed name of company to ROC for approval of name. The name shall not be resembled to any other company name.
Step-5: Upload the SPICe Forms INC-32, INC-33 and INC-34 in MCA (Ministry of Corporate Affairs) for incorporating the company.
INC-32 – It contains the details of the company like SRN of form INC-1, the type of company, the class of company, the category of company, sub-category of company, Company is Having share capital or Not having share capital, Main division of industrial activity of the company, Capital structure of the company, Registered office address, Particulars of individual first subscriber(s) cum directors, Particulars of payment of stamp duty, Additional Information for applying Permanent Account Number (PAN) and Tax Deduction Account Number (TAN) Information specific to PAN, Source of Income.
INC-33 (MOA) – It is a constitution of company which contains all the objects of the company. It is a document which describes activity and scope and relation with shareholders.
INC-34 (AOA) – It is a document which contains rules and regulations relating to the internal management of the company.
Step-6: Payment of Fees – After uploading above forms, registration fees shall be paid towards the registrar of companies online.
Step-7: Incorporation Certificate – When all documents are filed in order with requisite fees then MCA will verify it and issue the incorporation certificate. After this a company can start their business journey in the corporate world.
Essential documents required during the company registration
The following documents are necessary for company incorporation in India
- Self attested PAN Card (2 Copies) ( attested by gazetted officer or bank manager)
- Self attested Address Proof - Voter ID/Adhaar Card/ Driving License/Passport (2 Copies) (attested by gazetted officer or bank manager)
- 5 passport size photographs
- Self attested Bank Statement/ Electricity Bill/ Mobile Bill/ telephone Bill not older than one month (passbook copy is not accepted)
- Rental agreement and electricity bill of office address(Electricity bill not older than 1 month) if rented premises
- NOC (No Objection Certificate)
- BBMP tax paid receipt and electricity bill of office address (Electricity bill not older than 1 month) if own premises.
- Nature of Business
- 6 unique names of company
- Mail Id and Mobile Number of the Directors/Designated Partners
As you already know, all the above documents are important for registering a company for the better prospects. So once you have assembled all these documents you are ready to be incorporated your company smoothly.
--------------------------------------------------------------
Also Read More:
How to Form a Company in India Through SPICe?
How to Register an IT Company in Bangalore?
How to Register or Incorporate a Company in Bangalore, India?
Company Formation/ Registration/ Incorporation in India

The Indian government has come out with a new format for forming/ registering and incorporating companies in India. This particular format is being referred to as Simplified Proforma for Incorporating Company Electronically (SPICe). There are certain rules in India that are meant to govern these issues. For example in order to incorporate a Private Limited Company in India you need to have at minimum two members and two directors as well. In case it is a one person company there should be one member and one director. In any case a lot of information and documents need to be submitted in order to start a business in India.
The forms need to be filed during incorporating a business entity
While starting a business in India a company also has to file forms such as E-form INC-7, INC-22, and DIR-12. Normally, with all these formalities it takes around a month to get a company registered. However, the central government has made some major changes from 1st February onwards as far as the process of Company Incorporation is concerned. It is expected that this would reduce the time taken to incorporate these companies. The new process that it has started in this regard is known as “Incorporation through SPICe form”.
The background of SPICe act
It was on 1st October 2016 that the Indian government had amended Companies (Incorporation) Rules 2014 and also notified Companies (Incorporation) Fourth Amendment Rules, 2016. On 29th December 2016, the Indian government amended Companies (Incorporation) Rules 2014, and also notified Companies (Incorporation) Fifth Amendment Rules, 2016. All the changes came into play from 1st January 2017. Thanks to the amendment the process of incorporation became a faster through SPICe and can also use this form of incorporation in order to apply for PAN (Permanent Account Number) and TAN (Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number).
Information on SPICe
It is also referred to as E-Form SPICe (Form INC-32). The form deals with a single application that is meant to serve the purpose as far as reserving your company’s name, incorporating a new company, and/or applying for Director Identification Number (DIN) is concerned. You can also file the form even if the director does not have DIN. In this form at the most three directors would be allowed to fill up their respective details in order to file application for a DIN to be allotted to you. This can be done while incorporating a company.
E-Form SPICe (Form INC-33, INC-34) is to be filed with SPICe (INC-32) to get approve certified copies through MCA. E-Form SPICe (Form INC-33- MOA) which contains main objects of the Company and it also called as charter of the company whereas E-Form SPICe (Form INC-34 - AOA) which holds the rules and regulations available to the Company and subscription sheet has to be signed digitally by the promoters of the Company in MOA and AOA.
After the e-form has been processed and found to be complete the company would be registered and Certificate of Incorporation (CIN) would be allotted. The PAN would also be allotted as part of the CIN. Along with this, DINs are issued to director who does not have a proper and valid DIN as such.
How to fill up the form?
While filling up the form there are certain things that have to be kept in mind. First of all, you need to choose the kind of company you are trying to set up. The various choices that you have in this regard are New Company, Producer Company, Section 8 Company and Part I Company.
The next thing that you need to do is choose the class of company – private, one person, or public. The third step that you need to take is to choose the category of your company – would your company be limited by shares or would it be limited by guarantee or would it be an unlimited company. Herein, you also need to specify the applicable main division code with respect to the industrial activity that your proposed company would be a part of. You will also have to specify subscriber and authorized equity as well as the preference capital of your company, AO type for PAN and TAN with respective state codes, number of shares for each Director/promoter and last but not least attach all the required documents.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Related Posts:
Guideline for Company Registration in Bangalore, Karnataka
Difference Between Memorandum and Articles of Association

When we are going to incorporate a company we found there always a company has two important documents that is Memorandum of Association (MOA) and Articles of Association (AOA) which plays a vital role during the company formation. Here you can get a comprehensive package of information on MOA and AOA and their distinction.
So let’s come to know what is MOA and AOA
Memorandum of Association (MOA) and Articles of Association (AOA) are basically charter documents that are needed in order to set up a company and govern its operations thereafter. MOA can be described as the very basis on which a company is formed since it contains all the basic information about the company in question. AOA basically contains all the rules and regulations that would be governing the company when it starts to operate as a legal entity.
MOA is normally used in order to set up the constitution of the company and as such it can be called the cornerstone on which a company is built. AOA has the bye-laws that come into play in order to govern the internal affairs of the company.
You need to register both MOA and AOA with Registrar of Companies (ROC) at the time when you are incorporating the company.
Meaning and Definition of MOA
Memorandum of Association (MOA) is a special document that contains all the necessary fundamental information which is required for the company at the time of incorporation. It is the base of the company; it is also said in company law, no company can be incorporated without memorandum of association.
Memorandum is used to constitute the constitution of the company and it provides the foundation on which its structure is built by you. It defines the objects, powers and scope of the company activities as well as its relation to the outside world. The main objective of memorandum is to explain the scope of the activities of the company.
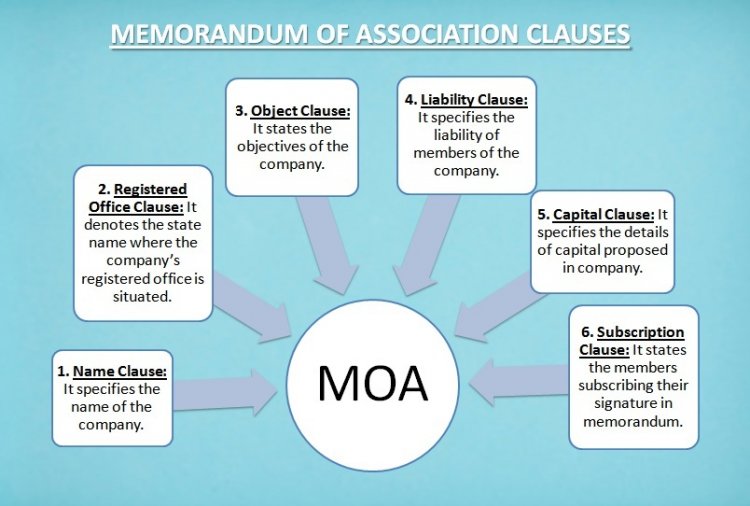
Special features of MOA
The main features of memorandum of association (MOA) are discussed below:
1. As far as MOA is concerned one of its most important features is the name clause. No company is allowed to register a name that the central government (CG) may consider to be an unfit one. At the same time, the name should not also resemble closely the name of another company.
2. The second important feature in this case would be the situation clause. As per this clause the company would have to specify the name of the state where you would be setting up the registered office of your company.
3. The third important feature of MOA would be object clause, whereby you would have to specify the prime objectives as well as the secondary objectives of your company as a business enterprise.
4. The fourth important feature of MOA would be liability clause. Here you would need to specify various details pertaining to the liabilities that the members of your company have at present.
5. In the fifth important feature of MOA – capital clause – you would need to specify the total capital that your company has.
6. The last major important feature of MOA is the subscription clause whereby you would have to specify the details of your subscribers, the shares that they have taken, and witness related details.
Objectives of Memorandum of Association (MOA)
As you know that Memorandum of Association is the foundation structure of a company; it defines the area where the company can operates. According to the Section 4(1) of Companies Act, 2013 memorandum of a company states that -
- The name of the company holds with last word "Limited or LTD" in the case of public limited company and "Private Limited or PVT LTD" for private limited company as well as one person company.
- The State in which where the registered office of the company is to be situated.
- The objects for which the company is proposed to be incorporated and any matter is considered necessary in furtherance thereof.
- The liability of members of the company, whether it is limited or unlimited.
Meaning and Definition of AOA
Articles of Association is abbreviated to AOA, is a primary/secondary document which states all the rules and regulations that designed by the company for conducting its policy of day-to-day administration to run their organization smoothly. Articles of Association define the rights, responsibilities, duties and the purpose of the members and directors of the company.
The articles of association is generally contains the provisions for the company name, Board of Directors, Equity and preference shares, Bonus shares, remuneration, ESOPS, the organization of the company, provisions regarding to shareholders meetings , Board meeting and committee Meeting, etc..
Special features of AOA
The major features of articles of association (AOA) generally deals with the following
1. AOA is basically a secondary document in a way. It spells out the rules and regulations of your company with regards to administration as well as daily management. Along with this, the article would also have the rights, powers, responsibilities, and duties of members as well as directors of the company.
2. It is optional for Public Ltd Companies on Limited by Shares; but compulsory for all other companies.
3. AOA also has information on audit and accounts of the company. It is very necessary for a company to have articles.
4. AOA also tells the classes of shares, their values and the rights attached to each of them.
5. It can be altered from time to time according to the company's activity.
Objectives of Articles of Association (AOA)
While the memorandum deals with external affairs of a company, the articles essentially deal with internal working of a company.
As stated in Section 5(1) Companies Act that the Articles of Association shall contain its bye-laws or rules and regulations for governing the management of its internal affairs to conduct the business of a company.
It deals with the rights of the members of the company among themselves.
In Section 5 (2), the articles shall contain such matters that may be prescribed and it can't be overruled. If it required necessary of additional matters in its articles then could be considered by its management.
The Table F, G, H, I and J of Schedule 1 of the Companies Act, 2013 contains the model articles, can refer to it as per Section 5(6) and companies may adopt wholly or partly these tables for company management purpose. [As it is mentioned in Section 5(7)]
The articles includes with some activities in a company are
- Share Capital
- Rights of Shareholders
- General Meetings
- Board of Directors and their responsibilities
- Accounts and Auditing
- Borrowing Powers and etc.
A Simple Comparison chart of MOA and AOA
Here take a look at the following main areas of differences between MOA and AOA during the formation of company:
|
MOA |
AOA |
|
MOA is defined in Section 2 (56). |
AOA is defined in Section 2 (5). |
|
It is subordinate to Companies Act. |
It is subordinate to the memorandum. |
|
It can be amended later on. |
It can be amended in some cases. |
|
It should have at least six clauses. |
You can draft it as per Rules and Regulations. |
|
It is mandatory for all companies. |
If you are a public company that is limited by shares you can use Table A rather than AOA. |
|
You have to file it for sure at the time of registration. |
You have to file it for sure at the time of registration. |
|
You need the approval of central government or Company Law Board (CLB) in order to alter it. |
Such approval is not needed in order to alter it. |
|
It defines the relation that a company has with outsiders. |
It deals with the relationship that a company has with its members as well as between the members. |
Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association are the necessary, most useful and important documents of the company which are to be managed to build the company’s aim, objects, power, scope, rules and regulations to run, grow and guide on various matters related to the company.
It also helps in proper functioning of management during the company life cycle. So, it is absolutely necessary and adds a great value for every company or business entity that’s why a company must have to need its own memorandum and articles for their business goals.
------------------------------------------------
Read Related Articles:
Procedure and Steps to Incorporate a Company in India
What is Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) and How to Get It?
Importance of Director Identification Number (DIN) and How to Apply It?
4 Major Benefits or Advantages of GST

Goods and services tax (GST) is one of the biggest fiscal reforms in India ever since Independence. It is expected that this indirect tax would have a major effect on businesses of all sizes, big as well as small. GST is expected to be levied on all goods and services and will take up the mantle now vacated by the indirect taxes of yore. This includes taxes such as excise tax, value added tax (VAT), and service tax to name a few. It is expected to have several advantages for Indian economy. Look over here, the four benefits of goods and services tax (GST).
1. Removal of cascading effect of taxes
This is expected to be an important benefit of the GST tax regime. It will significantly do away with the cascading effect that the previous indirect taxes had. In layman’s terms the phrase cascading effect of tax means one tax upon another. In the present regime the service tax that has been paid on the input services cannot be set off with respect to the output VAT. In GST the tax payer would be able to avail input tax credit without any problem whatsoever. This facility will be available across all goods and services. In the end this would reduce the tax burden applicable for the end user.
This will do away with the cascading effect. It is expected that this would really benefit industries where both products and services are involved. Examples of such businesses would be the various restaurants and eateries.
2. Greater tax breaks for smaller organizations
It is also expected that GST would make registration really easy. The registration limit for excise tax was INR 1.5 crores, and for VAT in most states across India the figure was at least INR 5 lakh. For service tax this figure went up to INR 10 lakh. The registration limit for GST is INR 20 lakh. In the states located in northeastern India this limit has been fixed at INR 10 lakh.
The present VAT structure makes it necessary for any company with an annual turnover of more than INR 5 lakh to pay the tax. The rates are however different across states. As far as service tax is concerned any company with a yearly turnover of at least INR 10 lakh would have to pay the tax. In GST this limit has been taken up to INR 20 lakh. It is expected that this would significantly benefit many small and medium industries.
3. Small businesses to be benefited by composition scheme
The administrators have also come up with an alternative programme of lower taxes that is expected to benefit the smaller companies that earn between INR 20 lakh and INR 50 lakh a year. This scheme is known as the composition scheme and would benefit these entities by reducing the tax rate applicable to them. It is being proposed that the limit be increased to INR 1 crore as compared to the earlier turnover threshold of INR 75 lakh a year. This is expected to be of significant benefit for a number of small businesses across the country as well.
4. Online procedure becomes much simpler
The whole process of GST is expected to be much simpler compared to other indirect taxes. This includes processes such as registration, filing of returns, and payment of the tax, all of which have to be done online. Now, there is no longer the need for a startup to do the rounds of a tax office so as to get registered for various taxes. The number of compliances has come down as well. At present, there are other indirect taxes such as excise tax and VAT that have their own compliances and returns. GST is expected to unify all the different compliances and returns and make the entire process much simpler and, thus, easier.
------------------------------------------------------------
Related Posts: